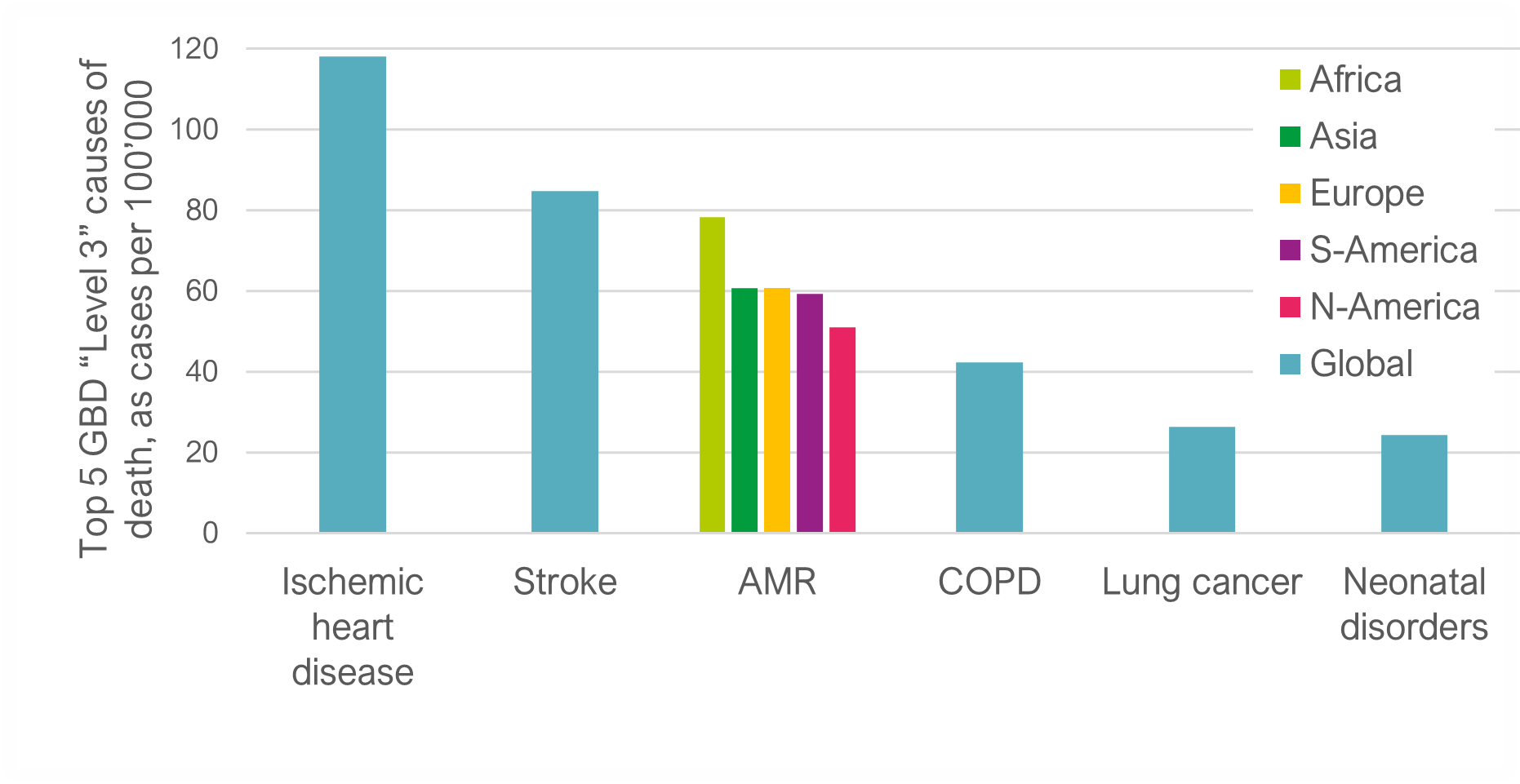
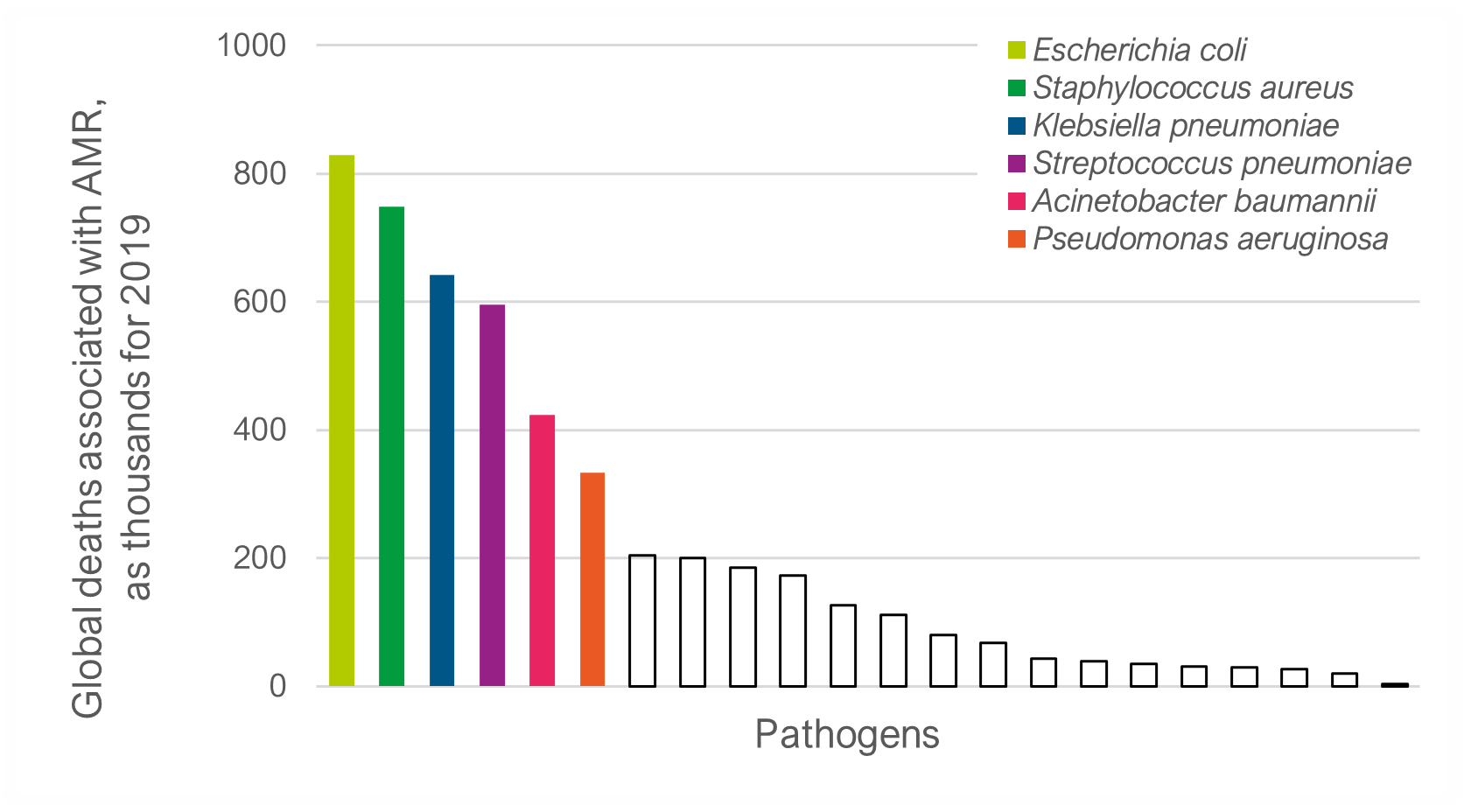
Five million deaths have been associated with bacterial AMR in 2019 as estimated by the Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators (1). Compared with all underlying causes of death in the Global Burden of Diseases 2019 AMR would have ranked third, corroborating the persisting global threat from AMR (2). Twice this number of deaths is projected for 2050, at a cost of US$ 100 trillion to the global economy through loss of productivity (3).
In the study led by the Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators, six pathogens were found responsible for more than 70% of deaths, including E coli, Staphylococcus aureus, K pneumoniae, S pneumoniae, A baumannii, and P aeruginosa. The WHO has also issued its list of priority pathogens to guide research and development of new antibiotics, where Gram-negative bacteria, including carbapenem- and 3GC-resistant Enterobacterales, P aeruginosa, and A baumannii have been categorized as critical priority (4,5).
At discoveric bio beta we develop novel antibody-based therapies addressing AMR in the treatment of serious lung and blood stream infections from Gram-negative bacteria.
Source: